A conservation project for rare toads in the StädteRegion Aachen

Habitats for yellow-bellied toads, common midwife toads and natterjack toads – plus many more
In a nutshell, what is it all about?
Within the framework of a LIFE project funded by the European Union, the Biologische Station StädteRegion Aachen e.V. would like to sustainably improve the situation of three endangered species of amphibians in the Aachen CitiesRegion.
Various measures are to lead to the long-term conservation of the species yellow-bellied toad, common midwife toad and natterjack toad in this region:
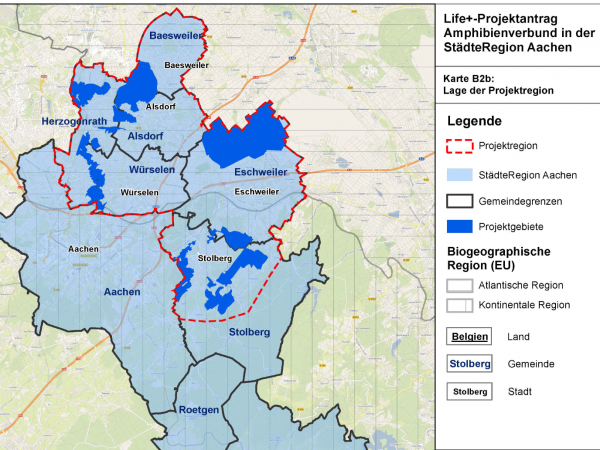
The existing habitats are to be improved and the occurrences linked by so-called stepping stone biotopes. New areas are also to be acquired for the protection of amphibians. Yellow-bellied toads that were previously bred from parent animals from the region are being introduced in two nature protection areas. During the duration of the project, team members will be observing the population trends of the animals to verify if the actions have achieved their aim.
To ensure the long-term protection of amphibians, communities, politicians, nature conservation associations, landowners and volunteers are involved in the project and advised on how to protect amphibians.
The project team offers local inhabitants a range of information such as guided nature tours, exhibitions and leaflets. Schools can take on a sponsorship and borrow educational materials. Members of the public can receive training to become an amphibian ranger and voluntarily take on the management of an area.
The leaflet of the project (only in german):
Facts, figures, dates
Duration: January 2017 to December 2025
Project partners: The Ministry for Environment, Agriculture, Conservation and Consumer Protection of the State of North Rhine-Westphalia (MULNV NRW) with the State Office for Nature, Environment and Consumer Protection of North Rhine-Westphalia (LANUV NRW)
Budget: Approximately Euro 4.2 million
Financiers: European Union LIFE Nature Programme, MULNV NRW, the Aachen CitiesRegion
Project region: Alsdorf, Baesweiler, Eschweiler, Herzogenrath, Stolberg, Würselen
LIFE
The LIFE Programme is the EU’s funding instrument for the environment, nature conservation and climate action. The current funding period 2014-2020 has a budget of Euro 3.4 billion. Of that, Euro 2.59 billion is allocated to the Environment sub-programme. The aim of the “Nature” section of that programme is to protect plant and animal species of European concern. The habitats and species of particular interest are listed in the annexes of the Habitats Directive and the Birds Directive.
The yellow-bellied toad, common midwife toad and natterjack toad are among them: for them and all other listed species and habitats a favourable conservation status is to be restored or maintained. This is assessed for various geographical regions. (The Atlantic and the Continental regions converge in the Aachen CitiesRegion.) The assessment of the conservation status takes into account the size of the population, the condition of the habitat, and any impairments in the area.
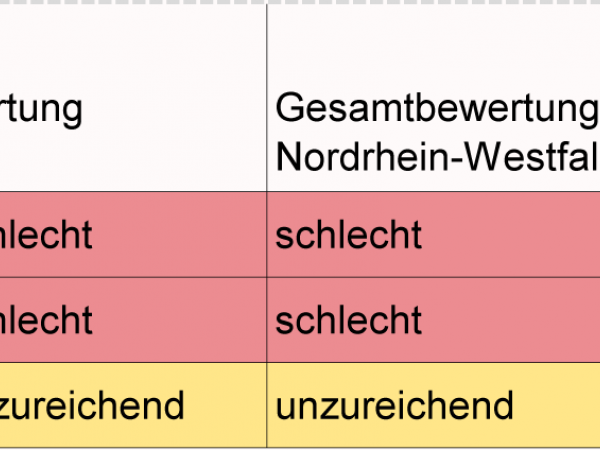
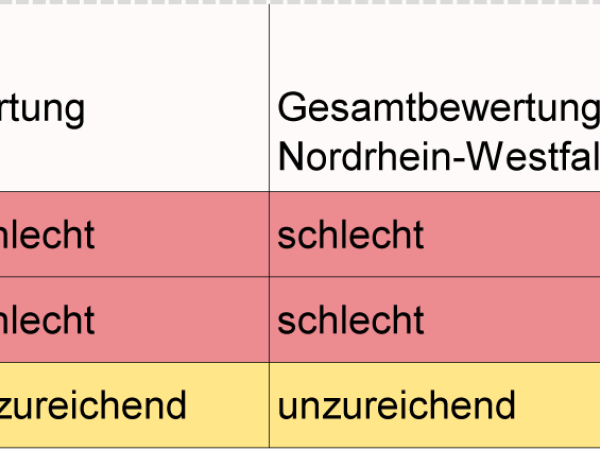
The conservation status of the target species in the Aachen CitiesRegion before the start of the project in NRW, and in Germany is presented below.
In the funding period 2014 to 2017, eight project proposals from Germany were approved in the category LIFE Nature, with two of those being projects of the Biologische Station StädteRegion Aachen e.V.: LIFE Amphibian Network and LIFE Development of a Habitat Network for the Violet Copper.

Conservation status of the target species
in the Aachen CitiesRegion, in NRW, and in Germany
The project aims to improve the conservation status of the target species in the Aachen CitiesRegion, thus contributing to the improvement of the conservation status throughout NRW. The EU Commission and the state of NRW provide financial means to do this.
In the funding period 2014 to 2017, eight project proposals from Germany were approved in the category LIFE Nature, with two of those being projects of the Biologische Station StädteRegion Aachen e.V.: LIFE Amphibian Network and LIFE Development of a Habitat Network for the Violet Copper.
Natura 2000
A special instrument for the maintenance of biodiversity is NATURA 2000, the network of protected areas that stretches across the European Union. Natura 2000 sites are protected under two EU directives, the Habitats Directive (FFH protected areas) and the Birds Directive (bird protected areas). The species and habitat types that are to be protected are listed in the annexes of these directives.
The Habitats Directive lists in Annex II “animal and plant species of community importance”, for which FFH areas must be designated, including the yellow-bellied toad. In the Stolberg region, for example, there are four FFH areas for the protection of the yellow-bellied toad.
Annex IV lists the animal and plant species that are under protection throughout Europe and for which a favourable conservation status is to be maintained or achieved. The yellow-bellied toad, natterjack toad and common midwife toad are listed here. All federal states, including NRW, are required every six years to determine and report to the EU the conservation status of the species.